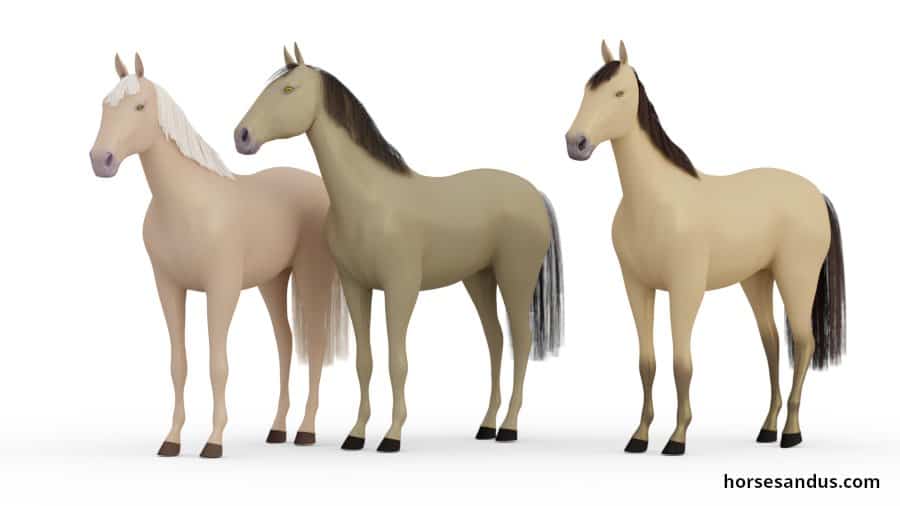
Buckskin and Bay Dun horses look very similar. They both have tan-colored coats with black lower legs, manes, and tails. But their colors are produced by different dilution genes (cream vs. dun). The main visible difference is the presence of clear primitive markings typical in dun horses.

Horse colors and patterns can sometimes look the same even when different color genes produce them. Buckskin and Bay Dun is one such case.
This article will highlight eight points of comparison (5 similarities and 3 differences) between these horses.
Before we continue, one important thing to consider is that we are comparing the Buckskin to Bay Dun. The other Duns – Black Dun and Red Dun- do not look at all like Buckskins.
5 Similarities between Buckskin and Dun Horses
There are a few similarities between Bay dun and Buckskin, which is why they often get mistaken for one another. We will look into the 5 main traits that they have in common.
1. Same Base Color
Both Buckskin and Bay Dun horses have the Bay base color. Although they have different dilution genes, the effect of these genes on the bay coat color is similar.
2. Diluted Coat Color
Both Buckskin and Bay dun have a diluted coat color, i.e., their coat color is produced by a dilution gene. However, these dilution genes are different in each of these horses.
3. Tan Colored Coats
Since Buckskin and Bay Dun have the same base color and have a dilution gene present, the resulting coat color is very similar.
In both cases, the red pigment of the bay color is diluted to a tan color, while the black pigment is not affected.
That is why they both have tan bodies with black lower legs.
4. Black Manes and Tails
The dilution genes of Buckskin and Bay Dun horses have the same effect on the black mane and tail of the Bay base color.
The result is black manes and tails in both cases.
5. Brown Eyes and Dark Skin
The dilution genes present on these horses do not affect the brown eyes and dark skin typical of the bay color.
So in both cases, they keep the same dark-colored eyes and skin of the bay base coat.
3 Differences between Buckskin and Dun Horses
We have seen the similarities between buckskin and bay dun horses, explaining why they get mistaken for one another. But what we really need to know is what makes them different so that we can tell them apart.
It can be difficult and, in some cases, even impossible to tell these horses apart just by looking at them.
Although there are 3 main differences between these horses, only one of them (the primitive markings) can be identified when looking at the horse. However, even in this case, we cannot be certain, and we will see why.
Let’s take a look at each one:
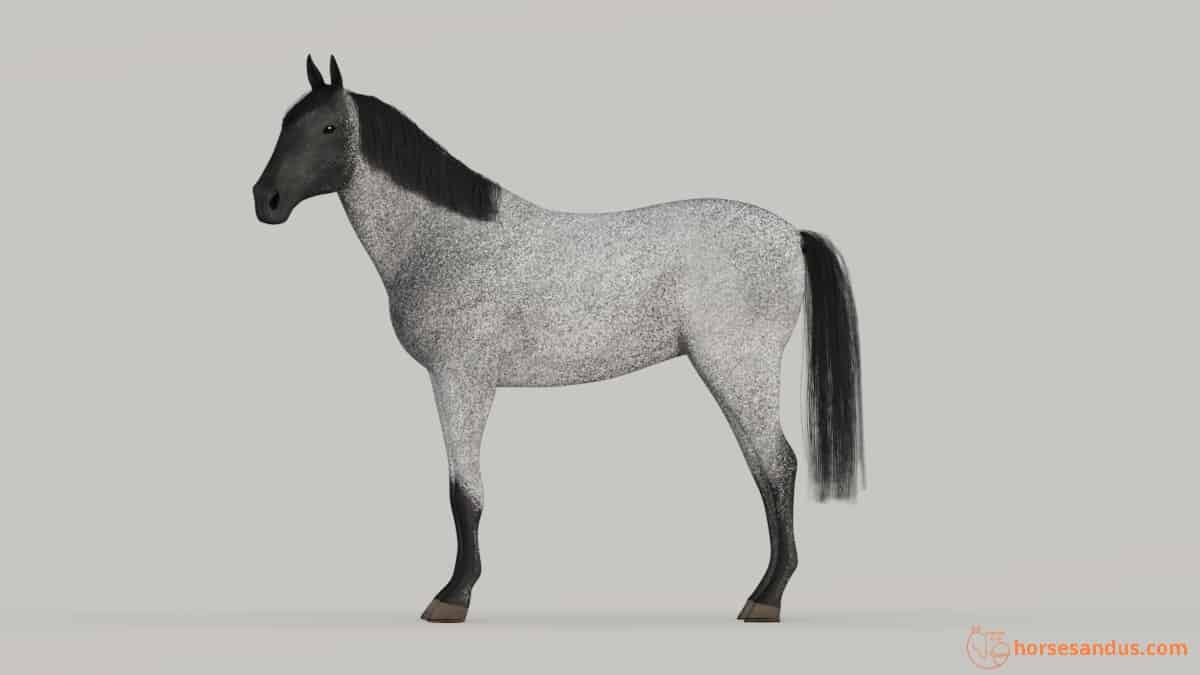
1. Dun Horses Have Primitive Markings
The Primitive markings are the main clue for differentiating a Bay dun from a Buckskin.

If we see a tan horse with dark points and with all these markings very clearly displayed with the dorsal stripe running all the way into the tail, then we can say it is a Bay dun horse.
On the other hand, if we see a tan horse with dark points without any sign of primitive markings, we can say it is a buckskin horse.
But it is not always that simple…
Sometimes the Primitive Markings May be Misleading
In some cases, primitive markings are also present in non-dun horses.
This is where it gets complicated…
Some non-dun horses may have a mutation of the dun gene (nd1), which is not actually dun but may display subtle primitive markings (pseudo-dun). Sometimes this can lead people to think that these horses are Dun.
Usually, the dorsal stripes in a non-dun horse do not fully extend into the tail, and the primitive markings are more subtle. This could be a way to tell them apart.
But the most reliable way to find out is to identify the dilution gene through genetic tests.
2. Buckskin and Bay Dun are Produced by Different Dilution Genes
The fundamental difference between these two horses is that two different genes produce their color dilution.
- The Buckskin is the result of one cream dilution gene on the bay base color.
- The Bay Dun horse is the result of the dun dilution gene on the bay base color
Unfortunately, we cannot always see this difference just by observing the horse, and so we may need to perform a DNA test to be certain.
3. Dun Horses Do Not Have Evenly Pigmented Hairs
An interesting and unusual fact is that the diluted hairs on dun horses are not evenly pigmented the whole way around.
There is a section of intense pigmentation along the hair’s length, on the side that faces outward from the horse’s body, while the side that faces inward has almost no pigment.
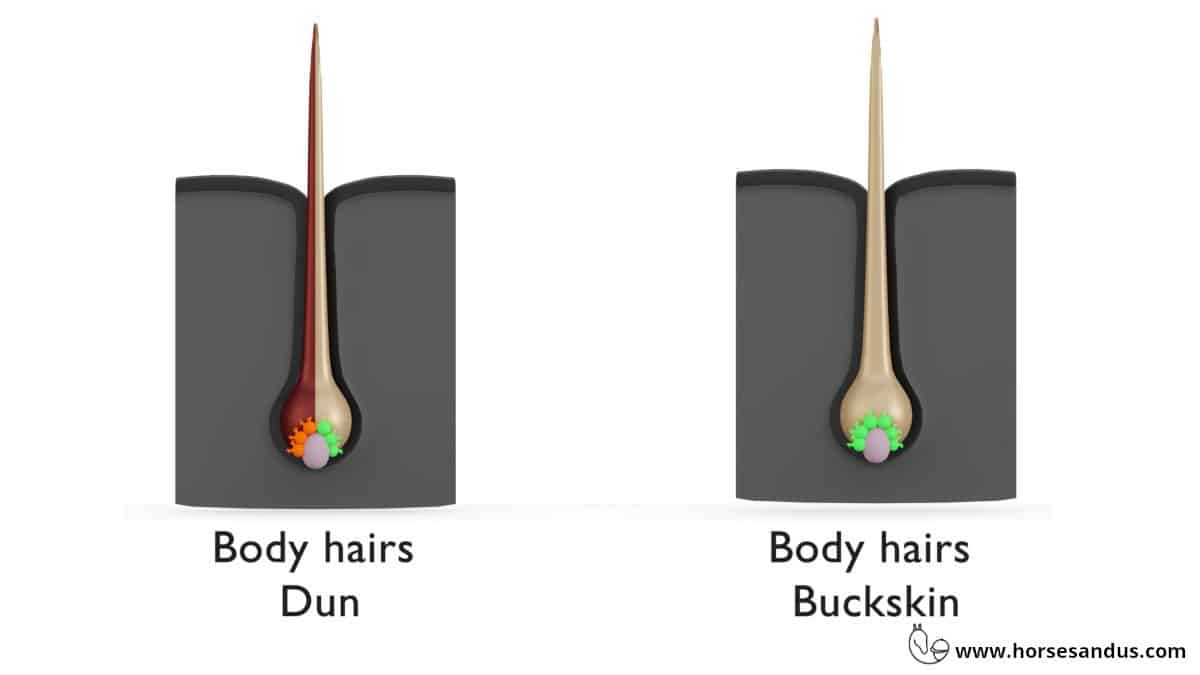
This trait is very unique and can clearly distinguish a Dun horse from other diluted horses.
Unfortunately, this cannot be observed just by looking at the horse. It would require a magnified view of an individual hair, which can only be done using a microscope.
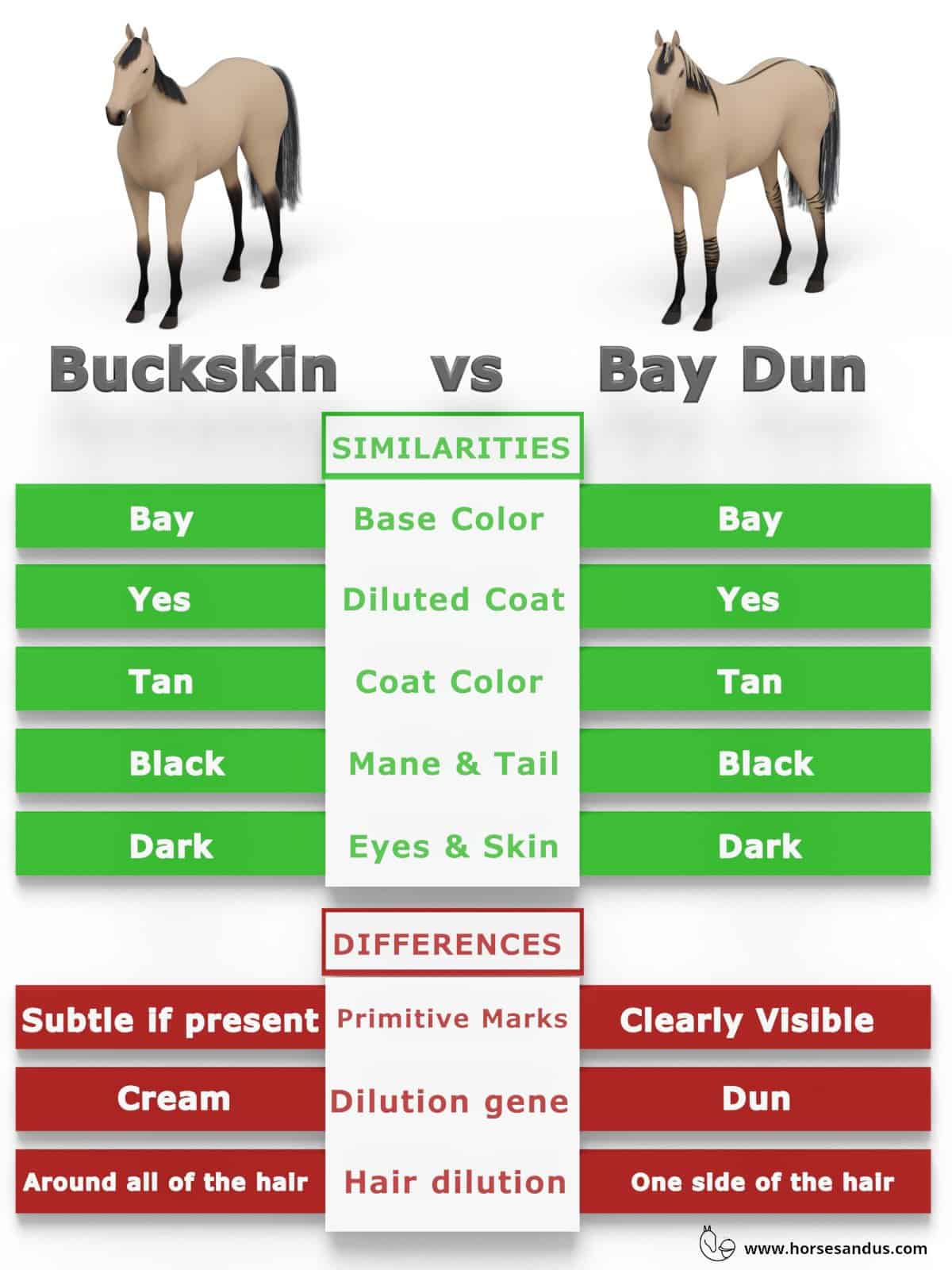
Buckskin vs Bay Dun Comparison Chart
What is a Dunskin Horse?
A Dunskin horse is a combination of Bay Dun and Buckskin. It has a diluted coat that results from the action of two dilution genes, the dun gene, and the cream gene.
A Dunskin horse has a light tan-colored coat and black points (mane, tail, and lower legs). The coat has a lighter shade of tan than a typical bay dun or buckskin because it has a combination of two dilution genes which have an additive effect. Although this may be an oversimplification because the shades of tan can vary a lot.
The primitive markings will also be present due to the effect of the dun gene.
The eyes and skin will be dark because neither of these dilution genes changes their dark color typical of its bay base color.
Conclusion
Buckskin and Bay Dun horses are often confused with one another because they have many similar traits :
- Same base color
- Diluted coats
- Tan colored coats
- Black mane and tails
- Dark eyes and skin
But they are not the same, so we can look for the differences to tell them apart.
There are mainly 3 differences, but it may be impossible to distinguish these horses just by looking at them.
- The main observable trait is the presence of primitive markings typical of a Dun horse. However some non-dun horses can also have primitive markings which makes this trait a bit tricky.
- The coat colors are the result of different dilution genes. Dun gene in the case of the Dun horse and cream gene in the case of the Buckskin horse. However this can only be identified through DNA tests
- The dilution of individual hairs is not the same. On a Dun horse this dilution is observed only on one side of the hair, while on a Buckskin the dilution is on the entire hair. However this can only be observed through a microscope.
So in some cases, we can tell these horses apart just by looking at them, but there are situations where we need to perform DNA tests to be sure.
Sources
Genetics of camouflage and the Dun pattern in horses: https://www.uu.se/en/research/news/article/?id=5896&typ=artikel
Radial asymmetric deposition of pigment in the growing hair: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/287646074_Regulatory_mutations_in_TBX3_disrupt_asymmetric_hair_pigmentation_that_underlies_Dun_camouflage_color_in_horses


